A Reuters survey of over a hundred economists shows that most believe the Federal Reserve will cut interest rates by 25 basis points at its policy meeting on December 9-10 to support a cooling labor market. This aligns with the November survey results and the nearly 85% probability of a rate cut in the futures market, but contrasts with the divisions among policymakers.
After a 25 basis point rate cut in October, Fed Chairman Powell warned of the risk of inflation rebound, emphasizing that a rate cut in December is not a certainty. Since March 2021, the inflation rate has remained above the Fed's 2% target. A 43-day government shutdown has hindered the release of key economic data, exacerbating inflation concerns. The minutes from the October meeting show significant divisions within the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), with some members leaning towards maintaining interest rates, and several opposing the October rate cut.
However, in a Reuters survey conducted from November 28 to December 4, 82% (89 out of 108) economists still expect a 25 basis point rate cut. Thomas Simons, chief U.S. economist at Jefferies Group, believes that the government shutdown leading to missing data has caused Powell to appear hawkish, but the situation may change in December, and a majority of Fed governors support continuing rate cuts. New York Fed President Williams also joined the rate cut camp, stating that rate cuts could provide 'insurance' against a labor market downturn without jeopardizing the inflation target.
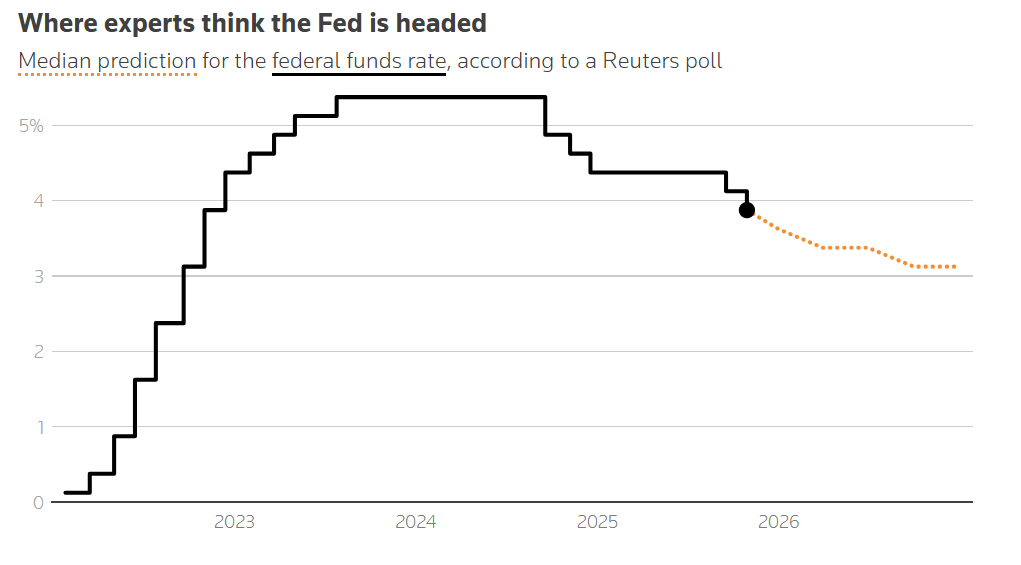
2026 Forecast: Lack of Consensus
The survey forecast for 2026 reflects a lack of consensus. Although the median forecast indicates two more rate cuts next year, with the federal funds rate reaching 3.00% - 3.25% by the end of the year, there is no majority opinion on the timing of rate cuts each quarter. Fiscal concerns, tariff uncertainty, and worries about the independence of the Federal Reserve are the main reasons. Kevin Gordon, head of macro research and strategy at Charles Schwab, stated that fiscal stimulus and tariff-driven re-inflationary forces will limit the Fed's actions next year.
Market Reactions and Inflation Expectations Gap
The conflicting signals from FOMC members accelerated the flow of hedge funds in the financial markets, as investors sought protection against policy uncertainty. There is a noticeable gap in inflation expectations, with the University of Michigan's consumer survey showing an inflation rate close to 4%, while market-implied indicators are much lower. Gordon pointed out that people's views on inflation are core, and 'affordability' is key. The median survey shows that the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index will remain above 2% before 2027.
Economic Growth Forecast
In terms of economic growth, the U.S. economy may grow by 3% in the third quarter, slowing to 0.8% this quarter, with an average growth rate of 2.0% expected over the next two years.