In the first two years of trading cryptocurrencies, I made about 10 million yuan with a principal of 10,000. I didn’t work after graduating from college. I spent all day watching videos and recording data.
1. The principal is 10,000 yuan. I did projects in college, affiliate marketing, shua orders, delivery, and APP filling various small tasks, and saved 10,000 yuan.
2. Enter the cryptocurrency world +, I think BTC is too expensive, so I've been playing with ETH +, ETH has leverage +, and then there are altcoin spot +. Choose coins,
Do a good job with position management. Just execute the simple idea consistently. When the market is not good, lose a little; when the market comes, earn a lot.
Why enter the circle?
If you want to change your destiny, you must try the cryptocurrency world. If you can't make money in this circle, ordinary people will have no chance in their lifetime.
I'd like to share my cryptocurrency trading strategy with you:
Many people start trading contracts with only 10,000 USDT (approximately 1,400 USDT) in capital, thinking, "I have a small amount of capital, so I'll just go for it."
But the truth is: the smaller the amount of capital, the more important position management is.
Large funds can be sustained by time, while small funds rely entirely on discipline. Otherwise, a single margin call will force you to rebuild your "faith" from scratch.
The following method is suitable for contract traders with capital between 5,000 and 20,000 RMB. The goal is not to double your money in a day, but...
Low drawdown, steady growth.
Let's put it this way: a job that earns you 10,000 yuan a month
However, in cryptocurrency futures trading, if you take 10,000 yuan as your initial investment and trade with a 100x leverage, a 1% increase in the price will earn you 10,000 yuan.
A 10% increase is 100,000; a year's salary in just a few minutes.
How many people do you think earn more than 10,000 yuan a month?
How many people earn 100,000 a year?
In the cryptocurrency futures market, besides highly skilled traders who use large sums of money to open small positions and hold them like spot traders...
All that's left are small-scale gamblers who get rich through leverage. In the cryptocurrency market, price fluctuations can be as high as 1-2% per second in extreme market conditions. If you're lucky, you can earn a month's salary in a second, or a year's salary in a few minutes.
Monthly salary: 3,000 yuan, annual income: 36,000 yuan, lifetime income: 1.44 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 4,000 yuan, annual income: 48,000 yuan, lifetime income: 1.92 million yuan
Monthly salary: 5,000 yuan, annual salary: 60,000 yuan, lifetime salary: 2.4 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 6,000 yuan, annual income: 72,000 yuan, lifetime income: 2.88 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 7,000 yuan, annual income: 84,000 yuan, lifetime income: 3.36 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 8,000 yuan, annual income: 96,000 yuan, lifetime income: 3.84 million yuan
Monthly salary: 9,000 yuan, annual income: 108,000 yuan, lifetime income: 4.32 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 10,000 yuan, annual salary: 120,000 yuan, lifetime salary: 4.8 million yuan
Monthly salary: 20,000 yuan, annual salary: 240,000 yuan, lifetime salary: 9.6 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 30,000 yuan, annual salary: 360,000 yuan, lifetime salary: 14.4 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 40,000 yuan, annual salary: 480,000 yuan, lifetime salary: 19.2 million yuan.
Monthly salary: 50,000 yuan, annual income: 600,000 yuan, lifetime income: 24 million yuan
Very few people earn more than 10,000 yuan a month, and even fewer earn more than 20,000 yuan a month. Most people earn less than 10,000 yuan a month. It feels like the money that ordinary people earn in their entire lives is only enough to buy a house!
From nearly losing 500,000 to over 25 million! I relied on the "10-minute quick trading strategy" to win passively in a volatile market for 4 years.
Six years ago, I only had 500,000 left in my account. I was chasing highs and lows in the crypto market like a headless fly, and I was about to lose all my savings. But through sheer hard work, I developed a "10-minute quick trading strategy"—now that Bitcoin is fluctuating between 100,000 and 110,000, this strategy is practically a lifesaver for beginners to avoid pitfalls in short-term trading.
Today I'm going to thoroughly analyze the core logic I've learned from four years of practical experience; it's all hard-earned, practical advice!
First, the key point: the short-term volatility in the crypto market is more exciting than a roller coaster right now. Determining buy and sell points within 10 minutes is the key to efficiency, but you must strictly adhere to 3 ironclad rules for entry. Don't act if you miss even one of them!
First, the RSI has fallen into the oversold zone (below 30) – which means it has bottomed out and the probability of it falling further is lower than winning the lottery.
Second, effectively hold above the short-term resistance line (such as the 105,000 mark for Bitcoin) – don't believe false breakouts, it's only reliable if it holds above the line for at least 3 10-minute candlesticks;
Third, the trading volume surged more than 3 times the usual amount – indicating that real money was entering the market, not just small fluctuations for retail investors to enjoy.
When it comes to leverage, I advise beginners to stick to 1-2 times! I still remember the scene in 2022 when I saw a friend use 20 times leverage, and a small fluctuation in the early morning wiped him out completely. His wife even wanted a divorce.
I grew my investment from 500,000 to over 75 million in 4 years, and I never used more than 2 times leverage. Those who dare to use more than 5 times leverage should tattoo the word "stop loss" on their foreheads.
The signals for opening and closing positions are so simple that even a fool could understand them: on a 10-minute candlestick chart, the lower Bollinger Band + oversold RSI is the "buy signal"; once you've made a profit, follow the rules. If you have 500,000 in principal and have made 50,000, you can only use a maximum of 15,000 in profit to add to your position, and you can't touch your principal at all—last year, I was greedy and held on for 10 more minutes, missing out on 30,000 in profit, and I still regret it now!
When taking profits, be decisive: sell 20% after earning 15% to lock in profits, and clear out your position immediately once the RSI exceeds 70 (overbought). Don't think about "going up a little more". In the crypto market, greedy people will eventually become the ones who get fleeced.
Different market conditions require different strategies; don't be rigid: In the current volatile market (Bitcoin fluctuating between 100,000 and 110,000): Divide your 500,000 into two parts, keep 250,000 as a base position, and use the other 250,000 for day trading (buy more when it dips, sell when it rises). Accumulating small amounts is more reliable than blindly chasing rallies. In a bull market (e.g., a one-sided upward trend): Hold 150,000 as a base position, and use 350,000 to ride the trend, but never chase the peak. Exit if it falls below the 5-day moving average. In a bear market (a one-sided downward trend): Hold 350,000 and use 150,000 for short-term trading to reduce costs. Don't try to buy at the bottom and end up buying at the halfway point. Those who try to buy at the bottom in a bear market end up being the ones left holding the bag.
Finally, there are the ironclad rules for survival. If you don't follow these three rules, even the most brilliant tactics will be useless:
① Divide 500,000 into 4 parts, and only use 125,000 for each transaction. Don't put all your eggs in one basket.
② If a single loss exceeds 2% (that is, 10,000), immediately cut your losses and never hold onto a losing position. I have seen too many people hold onto a loss of 10,000 until it grows to a loss of 100,000, and then their mentality collapses and they make reckless moves.
③ Never add to your position with your principal! Profits are fine, but your principal is the bottom line. If you break that line, you've lost everything.
Are there any brothers out there who, like me back in the day, held onto losing positions until 3 AM, watching their accounts shrink and cursing under the sun? Or are you a newbie who doesn't know how to set RSI or Bollinger Bands, buying high and selling low? Share your trading pain points in the comments, such as "not knowing how to read volume" or "always getting tricked by false breakouts," and I'll send you the details of setting up indicators in my trading strategy (how to adjust RSI parameters and Bollinger Band periods) privately!
Cryptocurrency Trading Essentials: The "Resonance" Rule Secretly Used by Institutions: Smart Money Uses Points of Interest (POI) + Fibonacci retracements to Locate the "Optimal Trading Zone," Making High-Probability Entry Points Undetectable.
In "smart money" strategies, Points of Interest (POIs) are key locations in the market where significant price action occurs. These locations are areas where institutional and retail investors make decisions. POIs can provide important clues about market structure, liquidity, and potential reversals or trend continuations.
Common POI types
1. Fair Value Gap (FVG)
A fair value gap (FVG) is a price inefficiency area caused by aggressive price movements, resulting in gaps between price action. The market typically returns to these areas to seek equilibrium.
FVG (Fixed-Variance Gaps) forms when prices move rapidly, causing gaps between candlesticks. The market often fills these gaps to restore balance.
When strong price fluctuations leave space between the highs and lows of adjacent candlesticks, an FVG (Free V Gain) pattern is formed.

These gaps indicate an imbalance between buyers and sellers, making them areas where prices may retrace.
Traders use FVG (Frequency Values) to predict potential pullbacks before a trend continues.
2. Order Blocks (OB)
The order book represents the area where institutions have placed large orders. Since smart money tends to return to these areas to fulfill orders, the order book (OB) often acts as support or resistance.
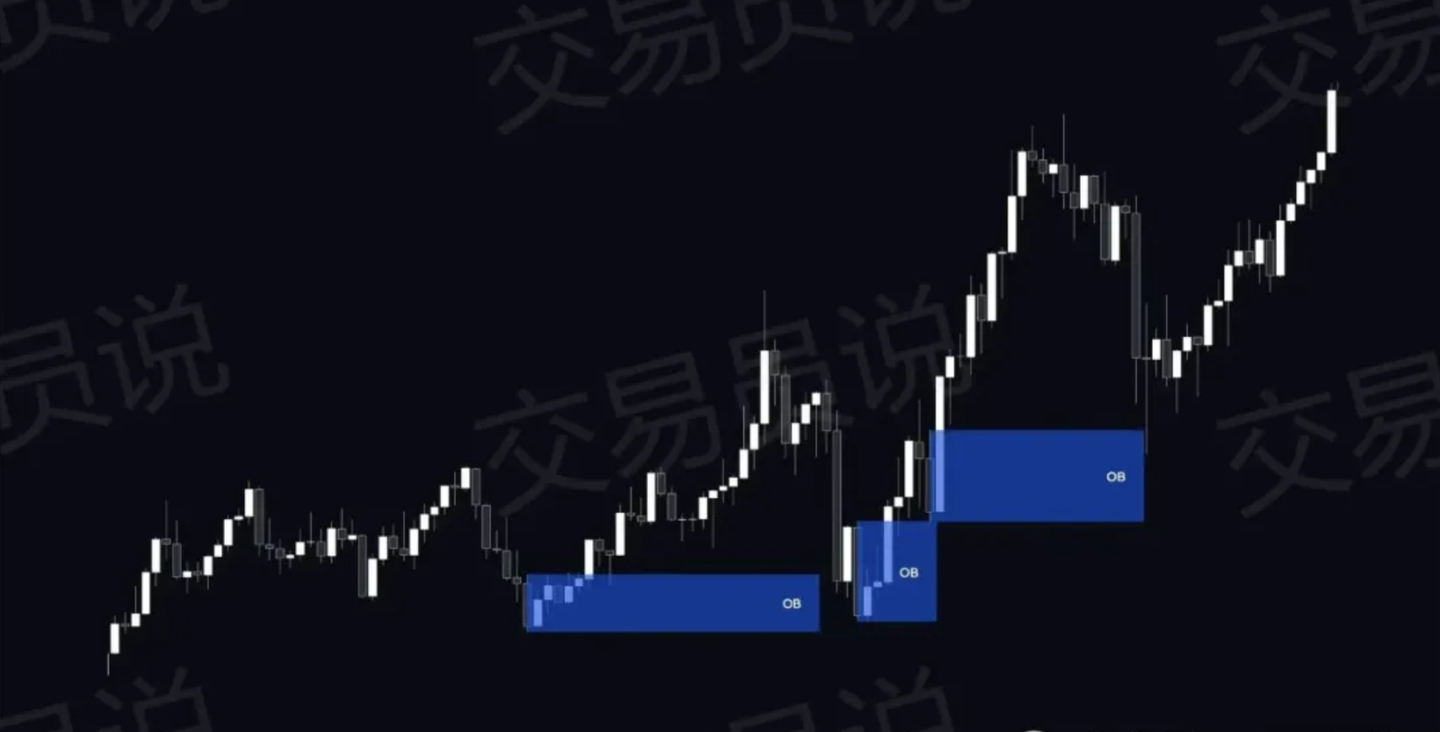
⊖ Bullish Order Block: The last bearish candlestick before a strong upward move. A buy opportunity typically arises when prices retrace to this area.
⊖ Bearish Order Block: The last bullish candlestick before a strong decline. Prices typically return to this area to provide a shorting opportunity.
Prices often retrace to order blocks before continuing in their original direction. Strong OB (On-Balance) patterns often overlap with liquidity zones and other converging factors, thus providing high-probability trading opportunities.
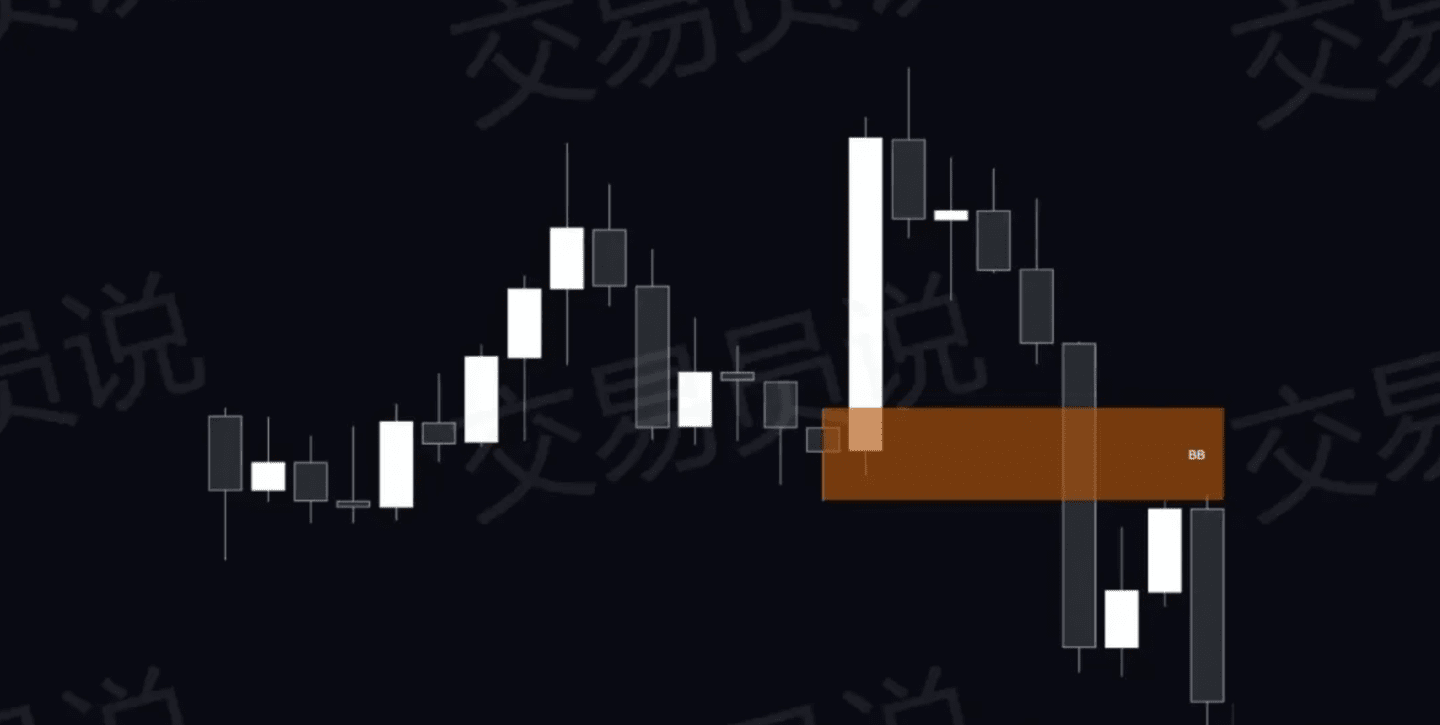
3. Destruction Block (BB)
Breaker blocks (BBs) are previous support or resistance levels that reverse roles after a strong price move. Breaker blocks indicate that previous liquidity has been absorbed, making them key areas for savvy traders.
⊖ Bullish Breakout Block: A previous resistance level is broken and then turns into support.
⊖ Bearish Breakout: A previous support level is broken and then turns into resistance.
When disruptive blocks are combined with liquidity zones and market structure, they can become a powerful resonant tool.
4. Reject Block (RB)
Rejection blocks (RBs) appear when the market strongly rejects a certain price level, typically leaving long shadows as a sign of a failed false breakout. These areas often become key price bands for smart money traders to watch.
RB indicates strong resistance or strong support, which often leads to reversals or trend continuations.
They typically appear near liquidity pools, where institutional traders trigger stop-loss orders or place pending orders.
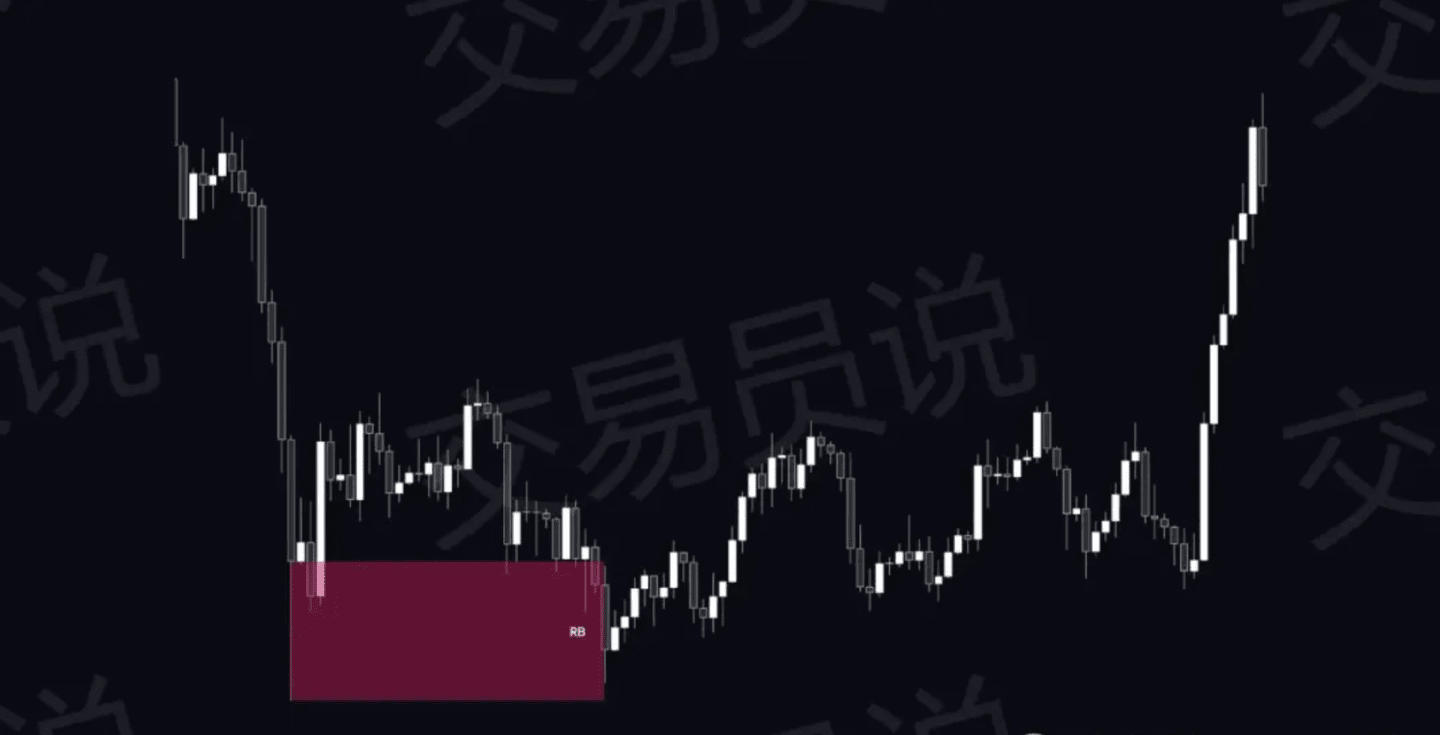
Smart money uses RB (Redundant Investor) to identify areas where prices may react, thereby optimizing entry points for high-probability trades.
When RB is used in conjunction with Fair Value Gap (FVG) or Order Block (OB), they can provide strong resonance support for trading patterns.
Why POIs are important
✍ Institutional trading activities: Institutions often execute orders at these key points, making them significant.
✍ Market Reversal and Continuation: POI helps traders predict potential turning points or trend continuations.
✍ Enhanced trading settings: When the POI coincides with a Fibonacci position, it can provide a high probability of trading opportunities.
Fibonacci trading and its role in Points of Interest (POI)
As is widely known, Fibonacci retracements are a commonly used technical indicator tool by traders, helping them identify potential reversal zones by measuring the depth of price pullbacks. When Fibonacci retracements coincide with Points of Interest (POIs), they provide a strong resonance for trading.
Application of Fibonacci retracements in trading
The Fibonacci retracement tool is used as follows:
⊚ Pull from the low point of the trend to the high point of the trend (used in an uptrend)
⊚ From the high point of the trend to the low point of the trend (used in a downtrend)
Key Fibonacci retracement levels:
⊚ 0.236 (23.6%) — Slight pullback level
⊚ 0.382 (38.2%) — Shallow pullback
⊚ 0.5 (50%) — Midpoint of the trend (Although not a Fibonacci sequence, it is widely used)
⊚ 0.618 (61.8%) – Golden Ratio; Strong Pullback Level
⊚ 0.786 (78.6%) — Deep pullback, often tested before a reversal.
Premium Zone and Discount Zone
⊚ Premium zone (above 0.5) – more suitable for finding short-selling opportunities
⊚ Discount zone (below 0.5) – more suitable for finding long opportunities
⊚ Equilibrium point (0.5 level) – Represents the fair price range
Points of Interest (POI) and Optimal Trading Entry Zone (OTE)
The optimal trade entry zone (OTE) lies within the 0.618 to 0.79 retracement range and is considered the most ideal high-probability entry area. When the POI and OTE zones overlap, the probability of a significant price reaction increases dramatically.

How do POI and OTE work together?
POIs mark key decision-making areas.
The trading pattern is stronger when the price retraces within the POI and enters the OTE area.
Institutional participants typically build or distribute positions within this range.
Steps to apply the Fibonacci sequence to POI
1. Identify market fluctuation points
Traders first identify key swing highs and lows on the chart. These locations form the basis for plotting Fibonacci retracements and assessing potential price movements.
2. Draw the Fibonacci levels.
Once key highs and lows are identified, traders use Fibonacci retracement tools to visualize pullback areas where prices may pause or reverse. These areas typically occur at key levels before a trend continues.
3. Find resonance with POIs
After drawing Fibonacci retracements, traders look for points of interest (POIs) that overlap with key retracement areas.
For example, if a bullish order block happens to be near the 61.8% retracement level, it may create a more probabilistic buying opportunity.
4. Confirm entry signal
When Fibonacci retracement levels overlap with Points of Interest (POIs), traders can optimize their trading strategies. They wait for confirmation from price action, such as bullish or bearish candlestick patterns appearing at significant Fibonacci levels overlapping with POIs, before deciding to enter a trade.
How to apply Point of Interest (POI) and Fibonacci in uptrends and downtrends
Uptrend (Buy Scenario)
#1. Confirm a Point of Interest (POI) (such as an order block, a broken block, a liquidity pool, or an FVG).
#2. Draw the Fibonacci retracement line from the low point of the band to the high point of the band.
#3. Find the best entry zone within the POI (OTE, 0.618-0.79 range).
#4. Enter the market after a confirmation signal appears (e.g., a bullish candlestick pattern or structure breakout of BOS).
Downtrend (Selling Scenario)
#1. Confirm a POI.
#2. Draw the Fibonacci retracement line from the high point of the band to the low point of the band.
#3. Find the OTE interval that overlaps with the POI.
#4. Enter the market after a confirmation signal appears (e.g., bearish price action or resistance rejection).
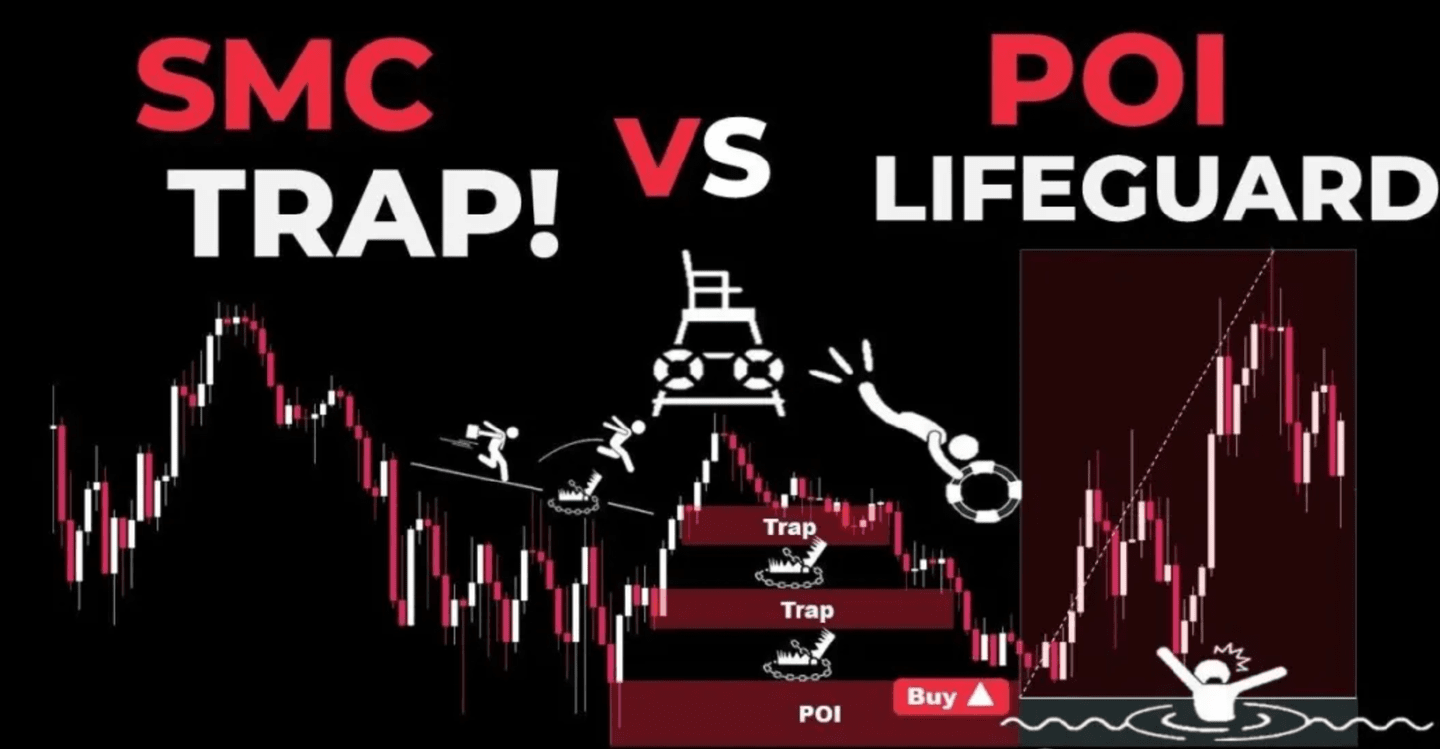
Common mistakes in using POI and Fibonacci
1. Expecting Fibonacci levels to always be effective
Not every pullback will conform to Fibonacci retracements. Price action and Point of Interest (POI) must provide additional confirmation.
2. Ignoring market structure and POI
Fibonacci retracements work best when paired with strong Points of Interest (POIs). Traders should analyze market structure before making any trades.
3. Over-reliance on Fibonacci as the sole reason for entry.
Fibonacci retracement should only be used as a confluence factor, not as the basis for trading decisions. Other technical and fundamental factors should also support trading decisions.
in conclusion
Combining POI with Fibonacci retracements can enhance trading models because it can:
1. Identify optimal entry points through key liquidity zones.
2. Improve the risk/reward ratio by utilizing high-probability reversal zones.
Providing multiple resonances between price behavior, liquidity, and market structure.
If you can understand and apply POI and Fibonacci, you will be able to make more rational judgments and seize more high-probability smart money trading opportunities.

Today I'm going to share some insights on position management in trading. Whether it's spot trading or futures trading, how you manage your positions directly determines your risk control level, average holding price, and final profit. This can be said to be the most important factor besides direction and mindset.
Position management has always been a very popular topic in trading systems. People are interested in how to adjust position size and add to positions to increase profits. Due to the many uncertainties in the market, tentative position building may be a safer approach. If you want to trade in the market and survive long-term, you must use position sizing to diversify risk and increase profits.
First, the olive-shaped averaging method
Assuming the price is about to rise, you first buy a small amount. Once you profit, instead of closing the position, you trade in increments several times the amount of the initial transaction. With sufficient funds, you buy in larger quantities; if the price continues to rise, you can invest all the remaining funds, adding small amounts at the beginning and end, and large amounts in the middle.
Second, the pyramid averaging method.
The most common trading method in the futures market involves initially buying a fixed position at a certain price. When the price rises to a certain level, a smaller position is purchased with less capital than the initial purchase. If the price continues to rise, an even smaller position is purchased, and so on, with each subsequent purchase gradually decreasing in size.
Third, the pyramid method of adding to positions.
This is the first test purchase with a small position. If the market rises and investors feel good, the next purchase will be larger than the first. The more shares you accumulate, the more funds you will gradually add.
Fourth, the method of adding positions in equal installments
Divide the invested funds into equal portions before each trade. As the market gradually rises as expected, add equal amounts of funds each time.
Fifth, the probability trading method
This method uses success rate as the profit criterion. There is no systematic money management approach for adding to or reducing positions in a single coin in batches. The result is either a stop-loss or a take-profit, both completing a round of entry and exit. For example, if an investor is bullish on a particular coin, they will buy a fixed position in that coin, liquidate it when the stop-loss level is reached, and take profit when the target level is reached. This is especially true for diversified participation in multiple coins.
Sixth, the Chase method – also known as the Martingale system – was originally used in casinos (roulette).
Its basic principle is: if you lose money, you need to double down your bet. If you win, you need to restore your bet to its original level. This will eventually make you profitable. This investment method is more suitable for large upward and downward trends.
Seventh, Antimartingale method
This strategy involves starting with a 1-unit percentage position. Each win doubles the position size, but each loss reduces it back to one unit. The advantage is low risk; adding to the position is based on profit, ensuring account safety. The disadvantage is that placing the largest position at the top inevitably leads to losses. This investment approach is relatively conservative and can be used at relative market tops and bottoms.
Eighth, how to add to your position after winning money.
You start with a few percentage units. Each time you exceed your stop-loss, you reduce your position by one unit; each time you win, you add one unit. Gradually increase your position! Ninth, Fixed Risk Increment Method
The number of additional positions and the amount of funds used are uncertain, but the potential risks are fixed.
Position management and detailed explanation of various methods for adding to positions
First, batch entry—that is, the concept of a surface—is a method of adding positions at different points.
This method is often referred to as overweighting. There are several ways to add to a position. The main method is to add to the position after certain conditions are met. Simple and common methods include fixed-point or proportional overweighting. That is, when your initial entry profit exceeds a set number of points or a certain percentage, you add to the position, and so on. However, the number of additions has its own efficiency. The more overweight, the better! Pullback Averaging Down – When entering a position, add to the long position when the price moves in the opposite direction. For example, when going long, if the index pulls back 50 points, add to the long position, and so on. In fact, there is often a delicate line between the amortized cost averaging down method and abandoning an order. If the exit method is not controlled properly, it can lead to terrible losses.
The profit and loss curve averaging method – simply put, is to add to your position when your profit reaches a set target, or when your loss reaches a set target.
Setting up an overweighting strategy involves using technical or custom indicators to measure market sentiment. For example, if ADX is used as the overweighting indicator, it can be used as the weighting indicator. For every 10 ADX increases, one more order can be placed, and so on. Of course, there are other methods to increase the amount; this only introduces some common ones.
Secondly, the concept of dynamically adjusting the number of points for each item is a method of adding weight to points with the same value.
This method is adjusted based on certain conditions or circumstances. Entry quantity is a dynamic position adjustment method. A common dynamic position adjustment method is to adjust the entry quantity based on the magnitude of volatility—the simplest method is position quantity = W / risk value, where W is usually a fixed value or a tolerable loss amount in points, and the risk value is a variable value, usually measuring recent volatility, such as volatility. Alternatively, W could be fixed capital, and the risk value could be the maximum consecutive loss of your strategy; this is also a possible approach.
The Martingale (flat betting) method—essentially a gambling strategy. In a betting market where you can only bet on either high or low, you continuously bet on one side (e.g., high or low). Each time you lose, you multiply your losses by the amount you lose the next time, until you win once, at which point you can recoup all your previous losses, winning more than your initial bet. If applied to trading, each trade only has two options: long or short. Whenever you lose money, your position size doubles the next time you enter the market. This method is generally unsuitable for the average person, as you must have substantial capital and the ability to withstand large losses to have a chance of winning.
Of course, there's also the reverse Martingale strategy, which is the exact opposite of the above—doubling down your position when you win. However, if you lose even once, all your previous winnings will be wiped out. This is just a loss of your principal. The biggest difference between the two in terms of timing is that the Martingale method is suitable for use in consolidating markets because general trading strategies in consolidating markets have a higher chance of loss. If the trading strategy has a greater chance of winning in a trending market, then using the reverse Martingale strategy might be better. These coding methods all have their limitations in use and are not suitable for the average person. However, you can still study them and take a look. It's quite interesting.
Special Circumstances Method – When you discover a certain situation and your trading strategy has a particularly high win rate, you can choose to add to your position at this time.
For example, the price recently fell below the 20-day moving average, but today it opened with a gap up above it. If you find this has happened a lot in the past, then this time is a good time. Increase your position size when entering the market, etc. Of course, there are many other ways to increase weight or adjust positions. However, translating some methods into a programming language and testing them back and forth isn't so easy. There will also be some limitations. There will be some limitations in the future, and I will backtest them when I have the opportunity to show you the differences.
Third, the number of lots can also be changed.
Sometimes, changing lot sizes involves money control issues, so there are many methods, such as pyramiding, inverted pyramiding, or even the same method as the Martingale overweighting mentioned above. You don't necessarily have to adjust your position based on 1, 2, 4, or 8 lots. You can also use Fibonacci numbers or any other method to adjust your position size, so adjusting the lot size is another step.
However, no matter how you adjust your position, it will always be related to the size of your available funds. You must determine your total position size based on your available funds; otherwise, you risk being liquidated.
Any method of adding funds will be closely related to the way you exit the market. Once you add to your position, the risk naturally increases significantly. Position management at this point determines when to exit the market. If you sell well, you can preserve your profits. If you don't sell well, your losses may increase, and it may be counterproductive. Therefore, different coding methods will have their corresponding ways of occurring. You must be extremely careful when writing programs, because the more complex the program, the more likely it is to have bugs. It will actually create a host of problems.
Therefore, when funds are limited, avoid putting all your money into a single scaling-up strategy, as this won't effectively diversify risk. Most scaling-up strategies are trend-based, and if the market is consistently consolidating, this approach will likely lead to significant losses.
Fourth, you don't need to rely on over-leveraging to diversify risk.
A good portfolio allocation should be diversified across multiple markets and strategies, using multiple markets to mitigate the risk of trading in a single market. Multiple strategies can be used to diversify the risk of trading certain commodities in only a single market. In fact, using multiple strategies can also achieve the effect of diversifying entry points, which is the same as scaling in. Moreover, using different strategies for entry has its own rationale, giving you more confidence when trading. While it's acceptable to use scaling in to test whether a trend has emerged, I recommend using multiple strategies and diversified entry points.
If you are still struggling in this cycle of margin calls, please force yourself to do these three things first:
1. Reduce transaction frequency:
2: Strictly implement stop-loss orders.
3: Don't let any small loss get out of control
If you're still feeling lost in the market and unsure of your next move, I'm here to share more specific strategies and mindset management methods. Opportunities are right in front of you; if you take the initiative, we can have a story together.
Investing is like a spiritual practice. Besides adhering to your investment philosophy in the face of drastic market fluctuations, you also need to develop a simple and easy-to-implement profit model. However, many novice investors don't know where to start. This resource, "Both Fish and Fishing," compiles solutions to frequently encountered problems in cryptocurrency spot and futures trading: (Essential Learning Materials for Cryptocurrency Traders). We hope our followers can find suitable methods for themselves and the learning methods they want to use, helping everyone build a clear and effective trading system.